Sagar Mandava
 Tomographic imaging systems are capable of probing the internal structure of objects and applications are found in diverse areas like astrophysics, geophysics, medical imaging, and industrial scanning. X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are two popular tomographic imaging systems that have revolutionized the world of medicine with their potential for non invasive diagnosis. In particular, MRI yields superb soft tissue contrast when compared with X-ray CT and provides structural and functional information related to the underlying anatomy. However, MRI systems are notoriously slow and sensitive to motion and patients are required to be still to avoid motion related artifacts. As most scans can potentially take tens of minutes to a few hours, decreasing the scanning time has the potential to reduce motion related problems and improve patient comfort. Reducing the scan time can also enable new applications that are currently not practical due to the temporal dynamics of the underlying physiology. Sagar works on problems in both CT and MRI. A common theme of his research is to accelerate scanning by forming useful images from as little data as possible. In MRI, his current research finds applications in cardiac MRI which is a challenging area owing to the motion of the heart and the flowing blood. Sagar’s work in CT is geared towards baggage scanning and evaluates several novel CT architectures that use far fewer measurements than traditionally fielded systems. This helps accelerate the scanning rate and improves the overall throughput.
Tomographic imaging systems are capable of probing the internal structure of objects and applications are found in diverse areas like astrophysics, geophysics, medical imaging, and industrial scanning. X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are two popular tomographic imaging systems that have revolutionized the world of medicine with their potential for non invasive diagnosis. In particular, MRI yields superb soft tissue contrast when compared with X-ray CT and provides structural and functional information related to the underlying anatomy. However, MRI systems are notoriously slow and sensitive to motion and patients are required to be still to avoid motion related artifacts. As most scans can potentially take tens of minutes to a few hours, decreasing the scanning time has the potential to reduce motion related problems and improve patient comfort. Reducing the scan time can also enable new applications that are currently not practical due to the temporal dynamics of the underlying physiology. Sagar works on problems in both CT and MRI. A common theme of his research is to accelerate scanning by forming useful images from as little data as possible. In MRI, his current research finds applications in cardiac MRI which is a challenging area owing to the motion of the heart and the flowing blood. Sagar’s work in CT is geared towards baggage scanning and evaluates several novel CT architectures that use far fewer measurements than traditionally fielded systems. This helps accelerate the scanning rate and improves the overall throughput.
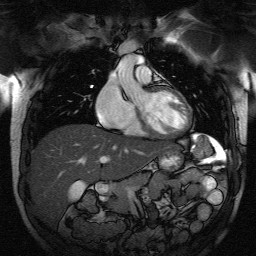
Sample Cardiac MRI scan

